
What is data mining?
New information and communication technologies as well as decision support technologies, by collecting, storing, evaluating, interpreting and analyzing, retrieving and disseminating information to specific users, can have a great impact on providing timely, correct and needed information to people. One of the tools used in these technologies is data mining. Data mining involves the use of advanced data analysis tools to discover valid patterns and relationships in large data sets. These tools are statistical models, mathematical algorithms and machine learning methods.
Data mining goes beyond data collection and management and includes analysis and prediction. Its other name is Knowledge Discovery in Database or KDD for short.


Concepts of data mining
In today’s highly competitive world, information has emerged as one of the important production factors. As a result, the effort to extract information from data has attracted the attention of many people involved in the information industry and related fields.
The high volume of constantly growing data in all fields, as well as their diversity in the form of textual data, numbers, graphics, maps, represent the complexity of the task of converting data into information.
In addition, the vast difference in data generation processes such as paper-based analog method and computer-based digital method has been added to the cause.
Several strategies and techniques have been used to collect, store, organize and efficiently manage available data and achieve meaningful results.
Advances in information science and information technology provide new techniques and tools to overcome the continuous growth and diversity of databases. These improvements have been achieved in both hardware and software aspects.
Data mining is one of the recent developments in data management technologies.
Data mining is a set of techniques that allow one to move beyond conventional data processing and help to extract information that is hidden or hidden in the mass of data.
The impetus to expand data mining emerged mainly from the business world in the 1990s.
Elements of data mining
Describing and helping to predict are the two main functions of data mining.
Data analysis related to selected characteristics of variables; past and present, and pattern understanding is an example of descriptive analysis.
Estimating the future value of a variable and projecting a trend is an example of the predictive ability of data mining.
In order to implement each of the two aforementioned functions of data mining, some basic but important steps must be implemented, which are as follows:
1. Data selection
2. Clearing data
3. Data enrichment
4. Data coding
Having the general objective in the study, selecting the main data set for analysis is the first necessity. The necessary records can be extracted from a data warehouse or an operational database. These data records are collected; They often suffer from what is called data pollution and therefore need to be cleaned to ensure format uniformity, duplicates are removed and domain consistency is controlled.
The collected data may be incomplete or insufficient in certain respects.
In this case, specific data should be collected to complete the main database. Appropriate resources should be identified for this purpose.
This process completes the data enrichment step. A suitable coding system is usually used to transfer data into a new structured form; It is suitable for data mining operations.

Data mining techniques
Some of the commonly used data mining tools are:
Query tools: Commonly used structured query language tools were initially used to perform preliminary analysis that could indicate avenues for further investigation.
Statistical techniques: The main characteristics of the data must be obtained by using various types of statistical analysis, including simple and cross tabulation of data and calculation of important statistical parameters.
Visualization: by displaying data in the form of graphs and photos such as a scatter plot; Grouping of data into appropriate clusters is facilitated. Deeper inference may be achieved by applying advanced graphical techniques.
Continuous Analytical Processing: Since data sets may have multidimensional relationships, there are several ways to combine them.
Case-based learning: This technique analyzes the characteristics of groups of data and helps predict each entity located in their neighborhood. Algorithms that employ an interactive learning strategy to explore a multidimensional space are useful for this purpose.
Decision trees: This technique retrieves different parts of the list of successful answers given for a query and thus helps in evaluating different options correctly.
Dependency rules: It is often observed that there is a close relationship (positive or negative) between a given set of data. Therefore, formal dependency rules are constructed and applied to generate new patterns.
Neural Networks: This is a machine learning algorithm that improves its performance based on application and evaluation of results.
Genetic Algorithm: This is another useful technique for target prediction. In this way, it starts with a group or cluster and its growth in the future by participating in some stages of the probability calculation process.
Random mutation: Plans as assumed in natural evolution. This technique can be implemented in several ways, and the unexpected or rare combination of factors that are happening and change the direction of the data design curve; reflects
The final step of the data mining process is reporting.
The report includes the analysis of the results and applications of the project, if they are used. and includes appropriate text, tables, and graphics.
Most of the time reporting is an interactive process where the decision maker plays with the data at the computer terminal and the printed form produces some possible intermediate results for immediate action.
Definition of data mining
Various definitions for data mining have been presented in academic texts, in some of these definitions data mining has been introduced as a tool that enables users to directly communicate with a large amount of data, and in others, more precise definitions have been introduced in which they explore Data is available.
Some of these definitions are:
Data mining is the process of extracting reliable and previously unknown, understandable and reliable information from large databases and using it in making decisions in important business activities.
The term data mining refers to the process of analyzing large databases in order to find useful patterns.
Data mining means: Searching a database to find patterns among the data.
Data mining means: Extracting large, reliable and new knowledge from large databases.
Data mining means: Analyze observable data sets to find reliable relationships between data.
As we can see in the different definitions of data mining, concepts such as knowledge extraction, analysis and finding patterns among data are mentioned in almost all definitions.
History of data mining
Recently, data mining has been the subject of many articles, conferences and scientific treatises, but these words had no meaning and were not used until the early nineties.
In the sixties and before that, there were fields for creating data collection and management systems, and research was conducted in this field, which led to the introduction and creation of database management systems.
The creation of data models and its development for network, hierarchical and especially relational databases in the seventies led to the introduction of concepts such as indexing and data organization and finally the creation of the SQL query language in the early eighties so that users can create reports and information forms. Create your opinion in this way.
The development of advanced database systems in the eighties and the creation of object-oriented, application-oriented and active databases caused the comprehensive development and application of these systems around the world. In this way, DBMSs such as DB2, Oracle, Sybase, … were created and a large amount of information was processed using these systems. Perhaps the most important aspect in the introduction of data mining can be considered the subject of knowledge discovery from databases (KDD) so that in many cases DM and KDD are used synonymously.
The concept of data mining was first proposed by Shapir. Subsequently, in 1991 to 1994, KDD workshops presented new concepts in this branch of science, so that many concepts became associated with it.
Applications of data mining in real environments
Banking:
Predicting credit card fraud patterns
Identification of fixed customers
Determining the amount of use of credit cards based on social groups
Insurance:
Claims analysis
Predicting the amount of purchase of new insurance policies by customers
Retail: One of the classic applications of data mining is the following:
Determining customer buying patterns
Market basket analysis
Predicting the amount of customer purchases by mail (electronic sales)
medical:
Determining the type of behavior with patients and predicting the success rate of surgery
Determining the success rate of treatment methods in dealing with difficult diseases
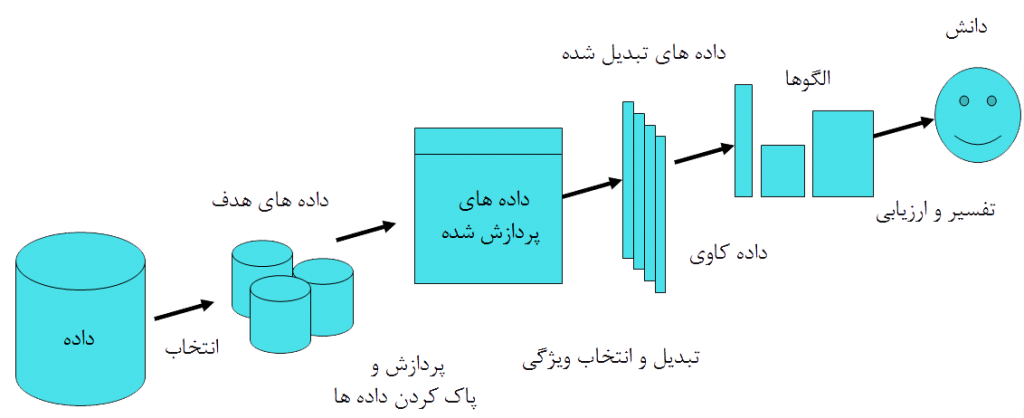
Steps in the process of discovering knowledge from databases
The process of discovering knowledge from databases includes five steps, which are:
Data storage
Data selection
Data conversion
Explore the data
Interpretation of the result:
As can be seen, data mining is one of the stages of this process, which as the fourth part plays an important role in discovering knowledge from data.
Data warehouse
Existence of correct and consistent information is one of the requirements that we need in data mining. Mistakes and the lack of correct information will lead to wrong conclusions and as a result, incorrect decisions in organizations, and will lead to dangerous results that are not few in number.
Most organizations have an information gap. In such organizations, information systems are usually built over time with different architectures and managements, so that a unified and specific information organization is not observed. In addition, for the data mining process, we need summary and important information in the field of critical decisions.
The purpose of the data storage process is to provide a unified environment for information processing. In this process, analytical and summary information is organized and stored in periods of time so that they can be used in decision-making processes that require data mining. In general, the following definition is provided for the data warehouse:
A data warehouse is a thematic, complex, time-varying and stable collection of data that is used to support the decision-making management process.

Data selection
Data warehouse contains different types of data, not all of which are needed in data mining. The required data must be selected for the data mining process. For example, in the database related to the store system, there is information about customer purchases, their statistical characteristics, suppliers, purchasing, accounting, etc. To determine how to arrange the shelves, only data about customer purchases and their statistical characteristics is needed. In some cases, it is not even necessary to explore all the contents of the database, but samples of elements may be selected and explored in order to reduce the operation cost.
Data conversion
When the required data is selected and the data to be explored is determined, usually certain transformations are needed on the data. The type of transformation depends on the operation and data mining technique used. Simple transformations such as converting one data type to another to more complex transformations such as defining new attributes by performing mathematical and logical operations on existing attributes.

Explore the data
The transformed data is explored using data mining techniques and operations to discover the desired patterns.


Advantages of data mining
Data flows into your business every day from a dizzying array of sources, in multiple formats, and at unprecedented speed and volume. Deciding whether or not a business is data-driven is no longer an option. The success of your business depends on how quickly you can uncover big data insights and incorporate them into business decisions and processes to drive better actions across your company. The success of your business depends on how quickly you can uncover big data insights and incorporate them into business decisions and processes to drive better actions across your company.
Data mining gives businesses an opportunity to optimize operations for the most likely future by understanding the past and present and making accurate predictions about what will happen in the future.
Data mining provides business benefits by increasing the potential to discover patterns, trends, correlations, and anomalies in data sets. A combination of conventional and predictive data analysis may be used to improve business decision making and strategic planning.




